![United Nations_ Sustainable Development Goals [dNASAb]](https://dnasab.net/wp-content/uploads/SDG_png_UN_ART.png)
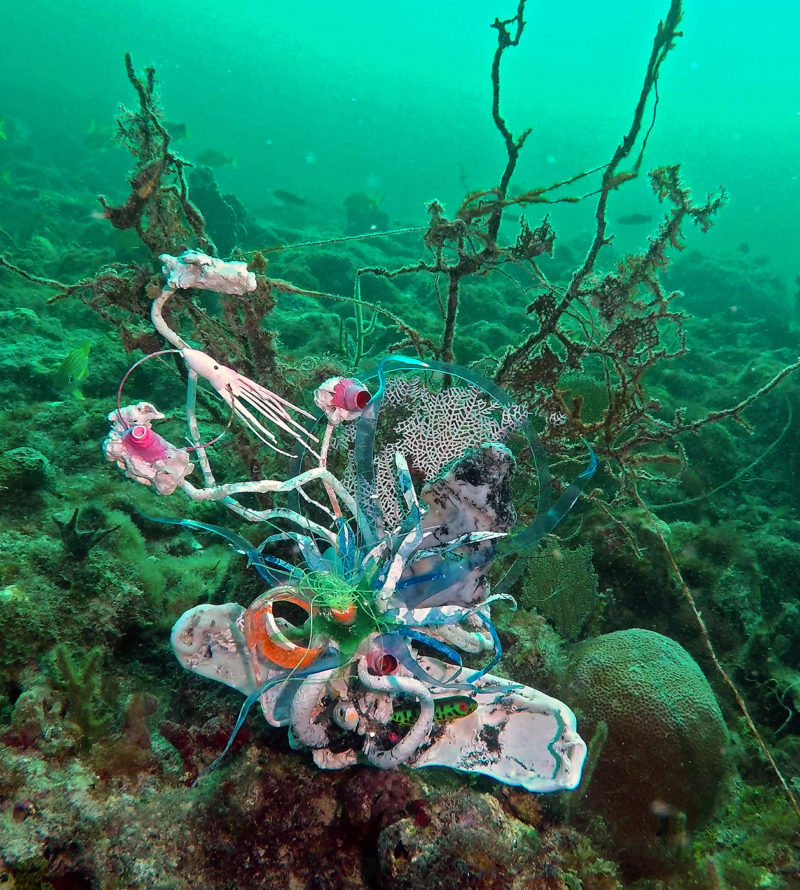
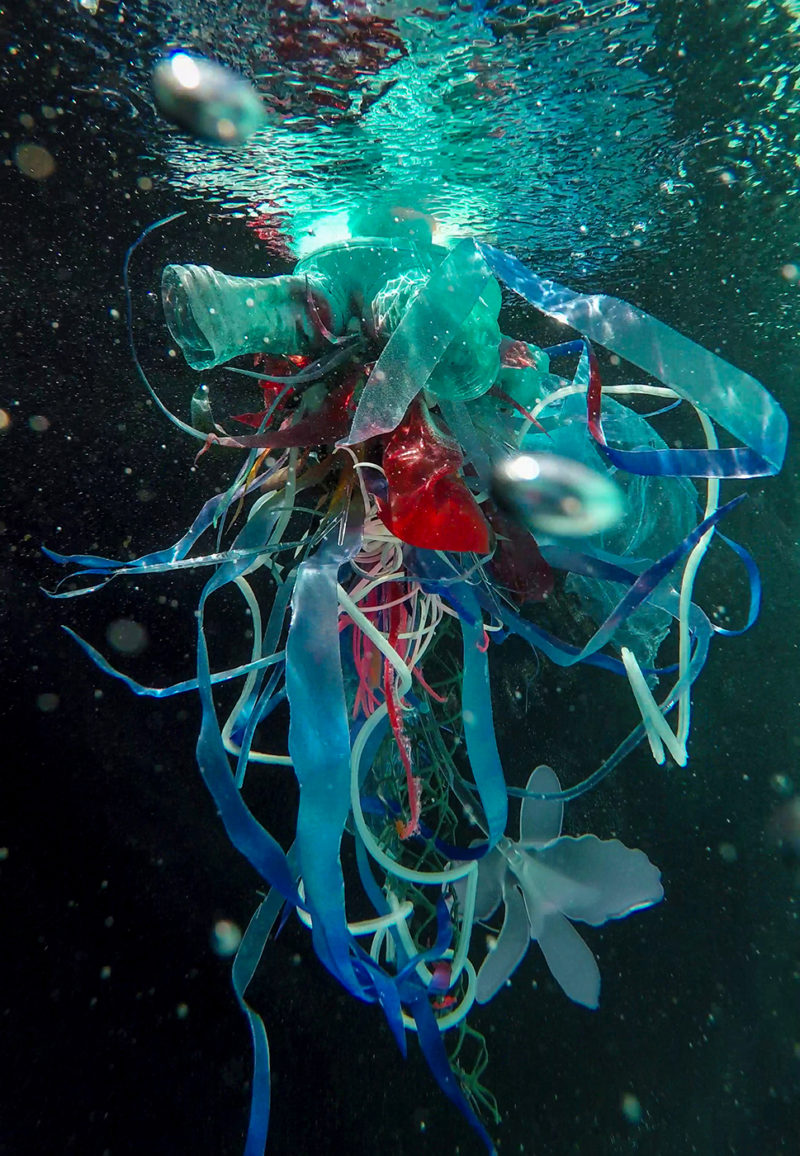
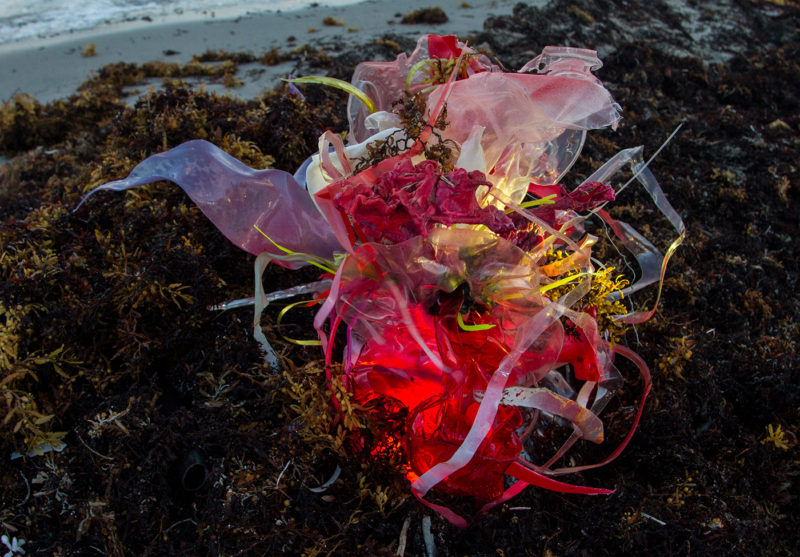
[dNASAb]’s work in the reclamation of Ocean debris, creating compelling sculptures with upcycled materials and single-use plastic reduction in Biscayne Bay, coupled with Environmental messaging and AR-XR experiences directly aligns the Art with the following SDG’s:
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: The practice of using upcycled and reclaimed materials directly supports reducing waste and promoting sustainable production.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: [dNASAb]’s focus on reducing the carbon footprint by minimizing waste and supporting environmental interventions through eco-friendly materials.
- SDG 14: Life Below Water: Environmental interventions in Biscayne Bay align with this goal by addressing plastic pollution and protecting marine ecosystems from further degradation.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Using advanced technology (like AI and AR) for environmental messaging contributes to sustainable innovation in storytelling and awareness campaigns.
![United Nations_ Sustainable Development Guidelines [dNASAb]](https://dnasab.net/wp-content/uploads/SDG_png_2a.png)
Marine Plastic Reduction Initiatives
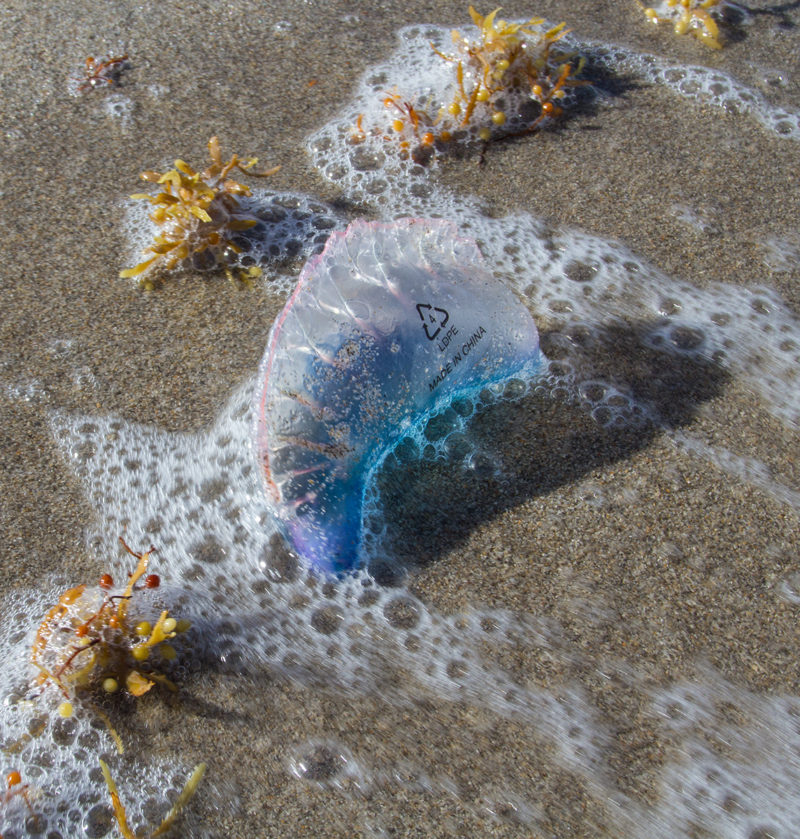
- Plastic Reduction at the Port: Advocate for policies within the Port of Miami and the cruise industry to reduce single-use plastics and encourage the use of biodegradable alternatives. [dNASAb]’s practice of creating sculptures from reclaimed materials could be integrated into this initiative as a visual reminder of plastic’s lasting impact on marine ecosystems.
- Install Ocean Cleanup Art: Collaborate with [dNASAb] to deploy your upcycled art as part of ocean cleanup awareness programs. These works, placed both in and around the waters of Biscayne Bay, can highlight the importance of reducing ocean waste and involve visitors in the cleanup process.
Advocate for Marine Ecosystem Protection Policies
- Policy Advocacy: Use [dNASAb]’s work as a platform to push for stricter regulations on waste management and plastic use in the cruise ship industry. Given his proximity to the Port of Miami and the fragile ecosystems in Biscayne Bay, He can advocate for waste reduction protocols and the adoption of environmentally responsible practices in port operations.
- Local Government and NGO Collaboration: [dNASAb] is working to align with organizations like the Biscayne Bay Task Force or Miami-Dade County Environmental Resources to implement projects that address the effects of plastic pollution and improve the health of the bay’s ecosystems.
![United Nations_ Sustainable Development Guidelines [dNASAb]](https://dnasab.net/wp-content/uploads/SDG_png_3a.png)
Intention to Collaborate with Local Port and Cruise Stakeholders
- Port of Miami Initiatives: Miami is a central hub for cruise lines, and the Port of Miami has a vested interest in sustainability. Collaborating with the port and cruise companies could involve creating public installations made from upcycled marine debris, positioned at the port as educational pieces.
- Cruise Industry Partnerships: Partnering with cruise lines that are working towards sustainability (e.g., those investing in clean energy or reducing single-use plastics onboard). [dNASAb]’s upcycled art could be featured in eco-conscious cruise programs, either as exhibitions onboard ships or at disembarkation points like the Port of Miami.
![United Nations_ Sustainable Development Guideline #9 [dNASAb]](https://dnasab.net/wp-content/uploads/SDG_png_5a.png)
Expand Technological Environmental Messaging
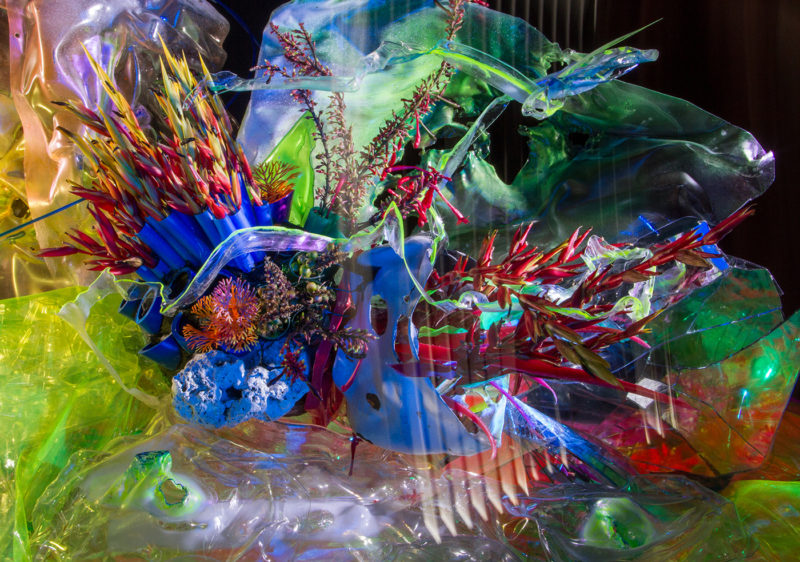
- Augmented Reality and AI-based Installations: Leverage the visibility of the Port of Miami to place AR-enhanced sculptures made from reclaimed ocean materials in high-traffic areas. This can raise awareness of ocean plastic pollution as passengers embark or disembark, directly connecting the marine environment around Biscayne Bay with their travels.
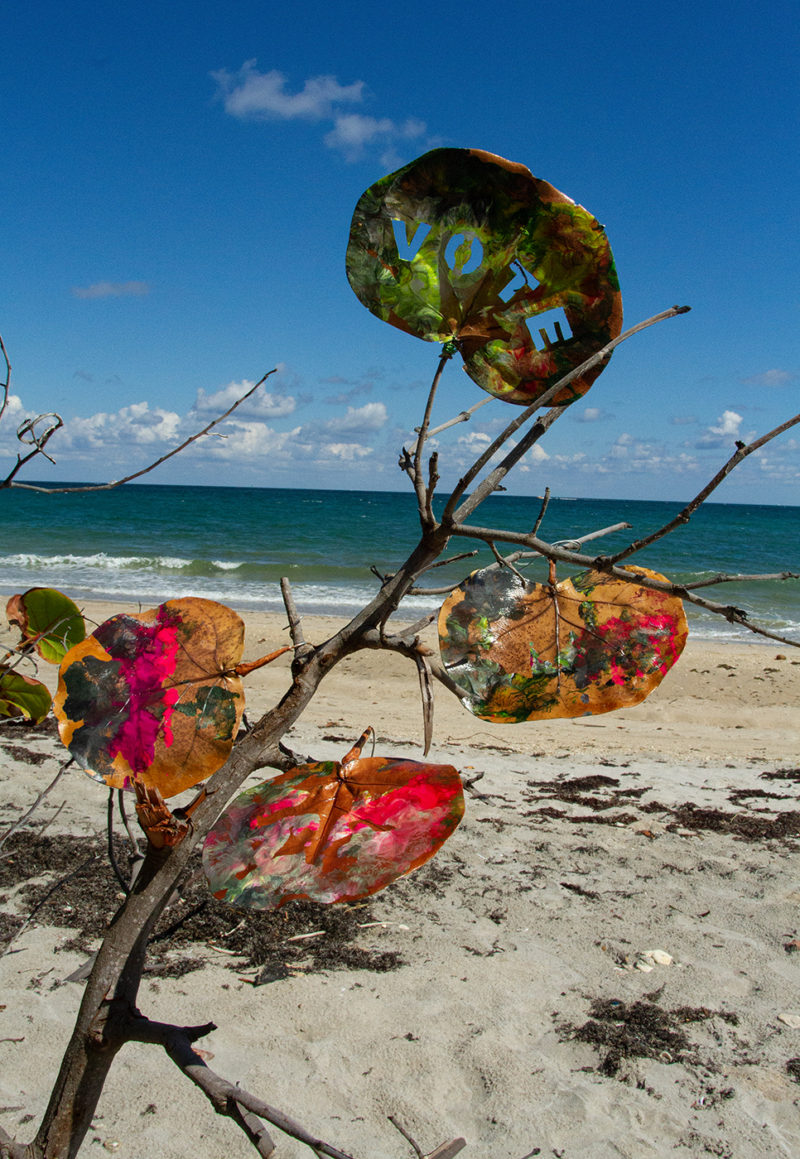
- Eco-Education: Develop AR experiences for cruise passengers, using Biscayne Bay and the Florida Keys as immersive case studies on the impact of plastic pollution. These AR experiences could be integrated into cruise excursions, teaching visitors about the local environment and your interventions in reducing plastics.
![United Nations_ Sustainable Development Guideline #12 [dNASAb]](https://dnasab.net/wp-content/uploads/SDG_png_4a.png)
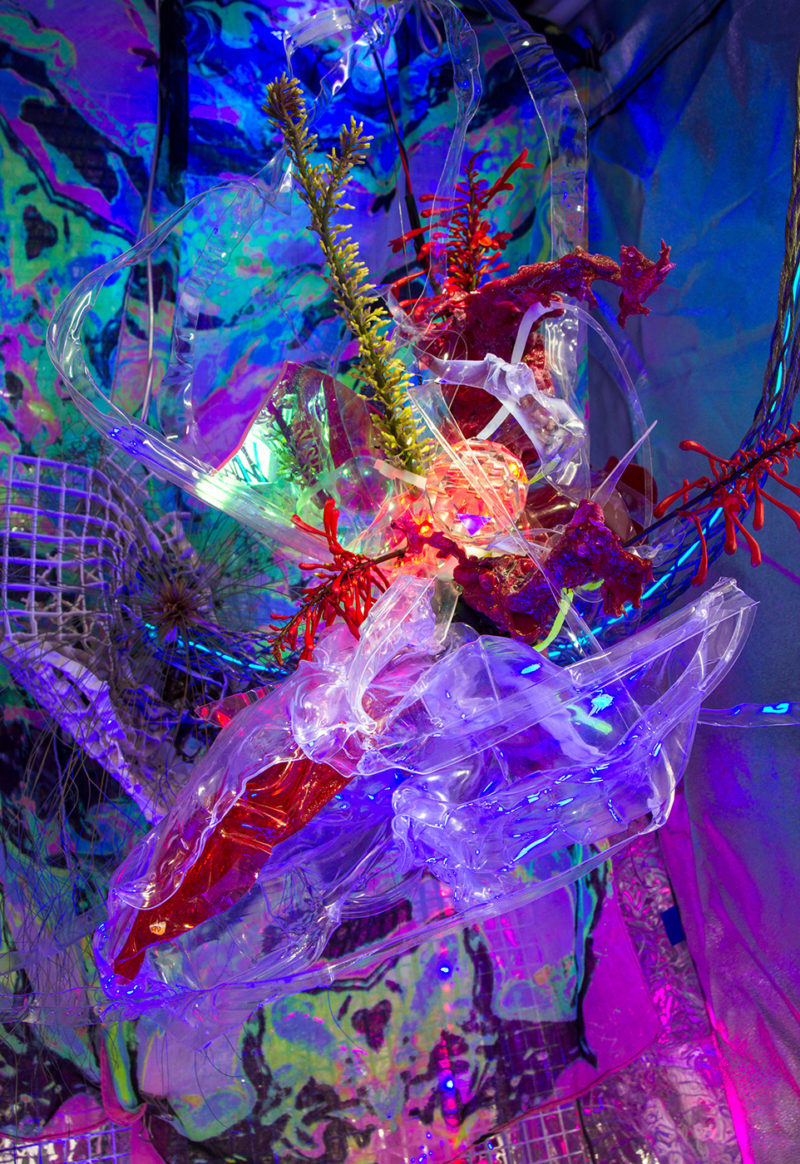
United Nations_ Sustainable Development Guideline #12 [dNASAb]SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: Your practice of using upcycled and reclaimed materials directly supports reducing waste and promoting sustainable production.
Showcase Projects in Public and Tourist Spaces
- Port Art Exhibitions: Place [dNASAb]’s environmental messaging and upcycled sculptures in public spaces at the Port of Miami to create impactful visual storytelling for tourists and locals alike. These exhibits can draw attention to ongoing marine debris issues and show how art can inspire action.
- Public Education Events: Task [dNASAb] to organize public workshops at the port or nearby areas where cruise passengers can engage with his art and learn about the process of upcycling marine debris into sculptures. This can be linked to sustainable tourism initiatives and port community outreach.
Connect to International SDG Initiatives
- Participate with [dNASAb] in UN conferences and events centered on sustainable tourism, oceans, and climate action, bringing attention to his local environmental efforts in Miami and the Port of Miami area. Together with [dNASAb] you can utilize his technological work in environmental messaging to present innovative approaches to SDG fulfillment.
By integrating artistic interventions with [dNASAb] the SDG goals focused on Miami’s cruise and port industries, can create a powerful connection between the local environmental challenges in Biscayne Bay and global sustainability efforts.